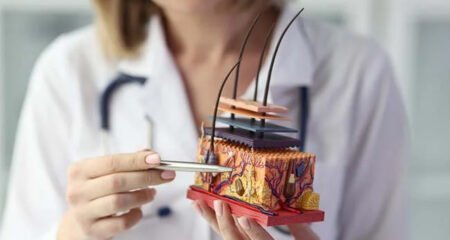
Connective tissue has an important function for humans because it can connect between tissues and many other essential functions. If you need help to select all that are examples of connective tissue functions, you can learn about connective tissue functions in this article. Also, learn some other things about connective tissue that are important for you to know.

Selecting Examples of Connective Tissue Functions
Without connective tissue, all tissues in the body cannot be properly connected. This is an important tissue that can maintain and protect all body tissues. Within the connective tissue, there are macrophages, fibroblasts, elastin, and many other important substances.
Connective tissue has an important role in ensuring that other tissues can work optimally. It keeps the body in the right position, stores energy reserves, and transports essential substances. If there is a problem with connective tissue, the body can lose its function.
Because it is made up of many types, connective tissue has many functions and each one is important. Here’s a list to select all that are examples of connective tissue functions:
1. Supports Body Elasticity
Organs in the body can stretch and then return to their original shape. This elasticity is essential for certain organs to perform their functions, such as the lungs. Connective tissue can support this elasticity so that the body can function optimally. Apart from the lungs, elasticity is also needed for ligaments, blood vessels, and other parts.
2. Structural Support And Connecting Body Parts
Connective tissue can connect tissues and organs while providing structural support. That is its most basic function. Tendons include connective tissue; their function is to connect bones and muscles, while ligaments connect bones.
Connective tissue can form a skeleton that can support many internal organs. It also forms capsules to surround organs to protect them. On the other hand, bone is also a connective tissue. Bones can support the body mechanically and serve as containers for muscles.
3. Regeneration Function
Regeneration is essential for the body and connective tissue has an important function to play. Fibrous tissue is a type of connective tissue, its function is important for healing wounds by producing scar tissue and collagen.
4. Protects Organs
Organs in the body must be well protected so that they are not damaged and can function properly. Connective tissue can protect body structures and organs from being damaged or anything like that. This tissue works by forming a layer to protect organs, especially vital ones.
In addition to forming layers, connective tissue is also able to support pressure or shock absorption by providing cushioning.
5. Supports Metabolism
Connective tissue can support metabolism by storing energy (fat). Cartilage is one of the connective tissues and has an energy storage function. It also supports glucose metabolism and stores minerals that are important for bone health.
Although cartilage has an important function for energy storage, it can also serve for organ protection as it can provide a protective cushion as well. So, some types of connective tissue can have multiple functions,
6. Transportation Function
Nutrient transportation is very important in our body. In addition to supporting nutrient transportation, connective tissue can also maintain body homeostasis. This tissue works by forming a medium that can support the diffusion of oxygen and nutrients.
Connective tissue also supports the regulation of the body’s electrolytes and helps detoxify the body.
7. Supports Immunity
In addition to supporting healing, connective tissue can also ensure the body is sufficiently immune by supporting immunity. Connective tissue can provide a place for immune cells to interact and migrate. One of the connective tissues, lymphoid tissue, can produce immune cells to keep organs healthy and fight off pathogens.
8. Thermoregulatory Function
Connective tissue also supports thermoregulation or regulating body temperature through thermal insulation as is the job of adipose tissue. Connective tissue functions also include distributing heat through blood circulation and other temperature regulation functions.
Connective tissue is a special tissue because it is important for connecting various important parts of the body. Connective tissue has other essential functions to support body functions. If connective tissue functions optimally, the health, function, and structure of the body can be maintained properly.
This tissue can ensure that our body can respond to various environmental factors and meet physiological needs. That’s the list of functions you need to learn if you need to select all that are examples of connective tissue functions.
Variations Of Connective Tissue: What Are The Types?
Because its functions are so diverse, the types of connective tissue also vary greatly. The various connective tissue elements including elastin, collagen fibers, and many other substances make this tissue of many types. Each type of connective tissue has an important function to support the overall function of the body.
There are at least four categories to describe connective tissue: proper, blood, bone, and cartilage. There are two kinds of connective tissue: dense and loose. To make it easier for you to select all that are examples of connective tissue functions, you must know what the types are.
Each type of connective tissue can have a different function. Here’s a complete list of connective tissue types:
1. Loose Tissue: Areolar, Reticular, and Adipose
Loose tissue is a type of connective tissue that receives messages and then connects tissues. There are many types of cells in this tissue whose main function is to transfer essential nutrients. In general, there are three types of loose tissue: reticular, areolar, and adipose.
Reticular tissue relies on its structure to support soft organs and other tissues. The function of areolar tissue is to support the body’s protection against infection. For example, areolar tissue can absorb excess fluid from inflamed areas. While adipose tissue mostly functions to store fat.
2. Dense Tissue: Elastic, Regular, and Irregular
In this dense tissue, there is less basic material but more collagen fibers. These characteristics make dense connective tissue more resistant and resilient, especially to stretching. There are regular and irregular dense tissues.
Regular tissue has parallel fibers so it is stronger while irregular tissue is more easily pulled in various directions. Irregular tissue can be found in the joint capsule and dermis. Another type of dense tissue is elastic tissue which can return to its original size after being stretched. Elastic tissue can be found in arterial vessels and the walls of the respiratory tract.
3. Liquid Connective Tissue: Blood
Blood is the only liquid connective tissue. The function of blood as a connective tissue is to carry oxygen and nutrients to all cells of the body. From the cells, blood will also transport metabolic waste. Blood contains a fluid matrix and certain cells.
In general, white blood cells, blood plasma, platelets, and leukocytes.
Although blood is a connective tissue, it does not connect tissues like other types of connective tissue.
4. Bone: Connective Tissue with the Hardest Structure
Blood is a fluid connective tissue while bone is the hardest structure. Because of these advantages, bones can protect various internal organs. Another function of bone as connective tissue is to support the posture or structure of the body.
Compact bone tissue has a dense structure, a smooth appearance, and is white as the outermost layer of bone. Compact bone tissue accounts for about 80 percent of bone mass in the body frame (adult body). In addition to compact bone, there is also spongy tissue in the inner layer.
As the name suggests, the spongy tissue in bones is lighter and has the main function of making room for marrow and blood vessels.
5. Cartilage: More Flexible than Bone
Compared to bone, cartilage is more flexible. Chondroblasts are specialized cells that build cartilage and this connective tissue is not composed of blood vessels. So, cartilage and bone have differences in hardness and vascularity.
Cartilage can be found in body parts such as the nose, ears, airways, and joints between bones. In general, there are three types of cartilage: fibrocartilage or fibrous, elastic cartilage, and hyaline cartilage. Hyaline cartilage can provide cushioning to minimize shock so that organs avoid damage. This cartilage is found in the larynx, trachea, ribs, and nose.
Elastic cartilage has more elastic fibers. It is very flexible but can still maintain the structure it supports. An example of elastic cartilage is the tissue in the earlobe. Fibrous cartilage can optimally withstand shocks because it is a combination of regular dense connective tissue and hyaline cartilage. There are also many collagen fibers in fibrous cartilage so that it can accept friction or mechanical stress well.
That’s a complete list of connective tissues, understanding some of these types of tissues can make it easier for you to select all that are examples of connective tissue functions.
Why Is Connective Tissue So Important?
Connective tissue has various advantages that make it essential for body functions. As a genetic specialist, I recommend taking good care of connective tissue because its function is so crucial to everyone’s body. Here are some of the reasons why we need to maintain healthy connective tissue:
- Supports vital organs
- Maintain body structure
- High flexibility, adjustments to body changes and movements
- Supports interconnection, providing a transportation path for various networks and organs
- Helps the production of blood cells (especially white blood cells)
- Stores and contains energy (fat)
Those are some of the advantages of connective tissue. Although it has many advantages, connective tissue also has disadvantages such as being prone to injury. If physical pressure is too much, inflammation, or tears can occur to the connective tissue. Although elastic, the level of elasticity in connective tissue is limited.
The body may not be able to fully recover after an injury due to limited elasticity. Moreover, problems with connective tissue can potentially lead to infection as it can harbor bacteria.
How to Care for Connective Tissue?
Not only is it important to select all that are examples of connective tissue functions, but you should also know the best way to care for connective tissue. If connective tissue is not properly cared for, it can make the body more susceptible to injury, and cause mobility problems. Here are some tips on how to take good care of connective tissue in your daily life:
1. Meet nutritional needs
You should consume a balanced diet of nutrients that are essential for connective tissue especially to heal the tissue when there is damage. Make sure you consume adequate doses of iron, vitamin C, and protein.
2. Maintain sleep habits
Maintaining adequate rest each day can support connective tissue recovery. If you have suffered an injury, adequate rest can speed up recovery.
3. Reduce swelling with compresses
Whether it’s a warm or cold compress, it can help reduce pain and swelling in the injured area. However, cold compresses are more recommended for that purpose as warm compresses are ideal for increasing moisture and maintaining blood circulation.
4. Avoid using skincare products
You can use care products but avoid those with too many harmful chemicals. Care products with irritants and alcohol can slowly damage the connective tissue.
5. Be wise in your activities
Sometimes you need to reduce physical activity. Excessive physical activity can prevent injury and speed up injury recovery. This is the discussion to help you answer the quiz, especially the question about select all that are examples of connective tissue functions.
FAQs
What is the main function of dense connective tissue?
Connective tissue is dense and can hold, protect, and support bones. Dense connective tissue or fibrous tissue includes the sclera, the inner layer of skin, tendons, and ligaments.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
The functions of this connective tissue are mostly physiological such as storing energy, absorbing shock, paracrine communication, and regulating body temperature. Adipose tissue also plays a role in providing cellular resources to support tissue renewal.
What is the function of reticular tissue?
Reticular tissue includes loose connective tissue. The function of this connective tissue is to provide structure to support the lymphoid organs, liver, and bone marrow.
What is the function of hyaline cartilage?
The characteristics of hyaline cartilage are smooth and slippery for bone support to move smoothly through joints. Although flexible, this cartilage is strong enough to maintain the shape of the joint.
What is the function of areolar connective tissue?
This tissue can hold organs in place and serves as a salt/water reservoir. Almost all cells get nutrients from areolar tissue and release waste into this tissue as well.
What is the function of a tendon?
The main function of tendons is to connect bones and muscles. Without tendons, we cannot move our limbs and are easily injured because tendons can absorb the impact on the muscles.
What are some examples of connective tissue functions?
If you need to select all that are examples of connective tissue functions, here’s the full list:
- Store energy reserves
- Transportation of substances
- Isolate and separate organs
- Protection
- Support
- Repairing tissue damage
- Bonding or connecting bones, muscles, and organs
AUTHOR BIO
On my daily job, I am a software engineer, programmer & computer technician. My passion is assembling PC hardware, studying Operating System and all things related to computers technology. I also love to make short films for YouTube as a producer. More at about me…